
Should we be worried about these types of technological advancements? No. For example, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or X-ray machines in hospitals perform functions that humans cannot do, but they complement human labor in the delivery of medical care. Moreover, it is important to keep in mind that not all technology displaces human labor. It also gives rise to new types of jobs-from auto repair workers in the past to computer engineers and web developers in the present. Should we be surprised that humans have invented increasingly complex machines to make production more efficient and cheaper? With each generation of technological breakthroughs, this is to be expected, as that is the very definition of human progress. But this is to be expected, as technology has evolved from electricity and computers to quantum computing and artificial intelligence (AI). But there is one aspect of the 4IR that is different than before: Increasingly complex tasks can now be automated (Autor 2015, Acemoglu and Restrepo 2018, ADB 2018). The technology of today will have similar effects it is not evident why things would be different this time.
#HISTORY OF AUTOMATION AND JOB LOSS SOFTWARE#
They gave rise to occupations that did not exist before, such as electricians, electrical engineers, computer engineers, software developers, website designers, etc. But, is it different compared with technological innovations in the past? Economic history tells us that the invention of electricity and computers impacted all sectors and industries and spread across the globe. For example, blockchain, which is “a digital, distributed ledger that keeps a record of all transactions across participating peer-to-peer networks,” is set to transform businesses worldwide. There is one question that is on everyone’s mind when it comes to the 4IR: Is this time different? As new technology allows us to automate increasingly complex tasks, should we finally be worried that “technological unemployment,” as was warned by luminaries such as David Ricardo, Karl Marx, and John Maynard Keynes, would be borne out in the near future?Īs computing capacity improves and becomes cheaper, its usage in production and delivery of services will spread across industries.

1 The future of work globally is tied to labor market outcomes in Asia and the Pacific-in fact, there is no other region in the world that highlights the challenges and opportunities that stem from the 4IR better than Asia. The Asia and Pacific region is home to more than 60% of the global working-age population, and six out of ten young people in the world today live in this region.
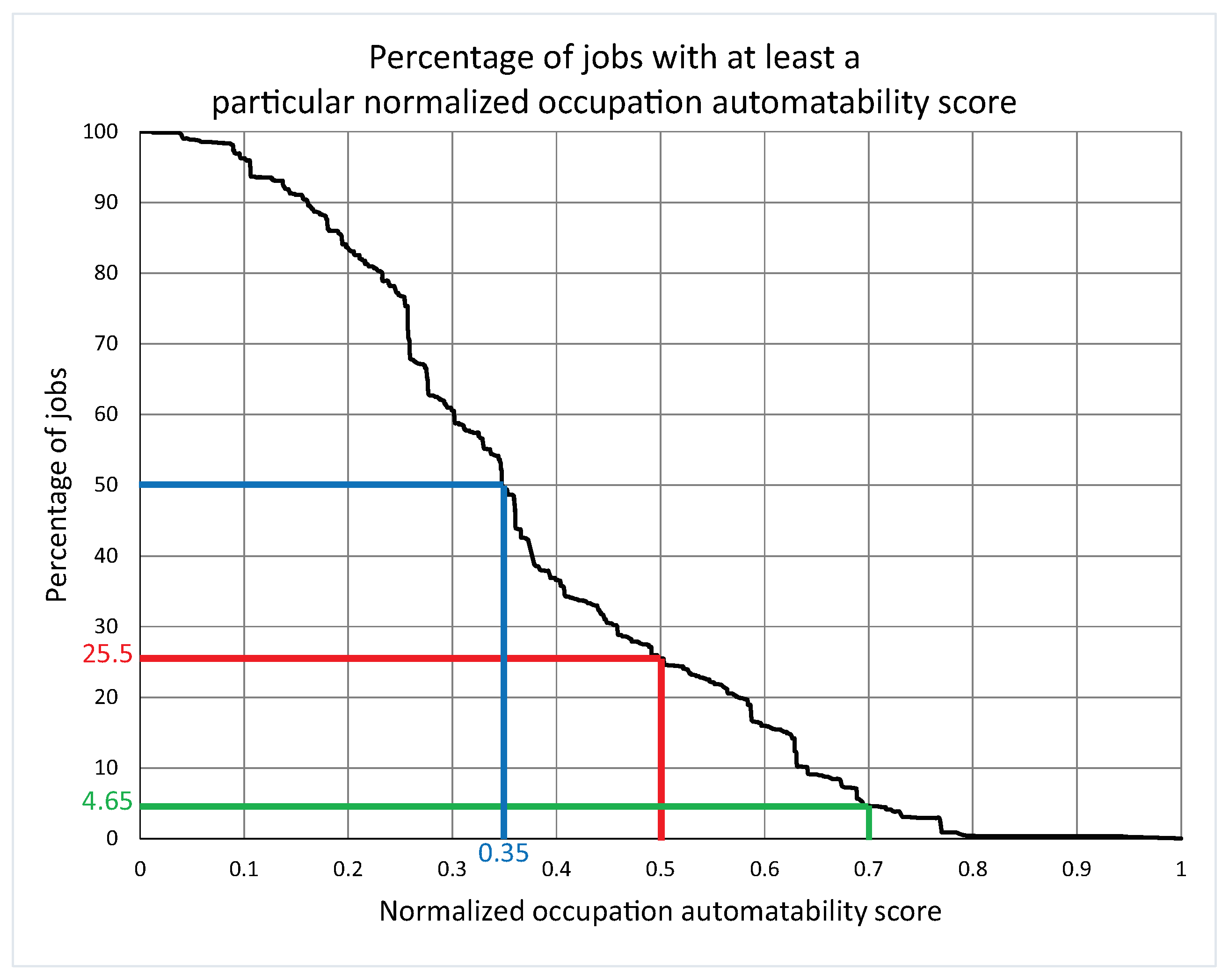
While displacing some jobs in their wake, new technologies will simultaneously unleash countervailing forces that generate more jobs, and the net effect at the aggregate level will be positive. Recent studies, discussed below, show that new technologies will result in higher productivity. Just like the industrial revolutions preceding it, the 4IR will profoundly affect people’s lives.Īs the 4IR unfolds, some types of jobs will disappear, while many others will be created. Throughout history, humans have always endeavored to produce things better, faster, and cheaper: from the use of water and steam power to mechanize production in the First Industrial Revolution, to the use of electric power for mass production in the Second Industrial Revolution, to the use of electronics and information technology to automate production in the Third Industrial Revolution, and to the extreme automation, connectivity, and the wider implementation of artificial intelligence in the 4IR.

In this essay, we examine the literature on how the 4IR is changing the demand for jobs and explore the implications of new technology on jobs in Asia and the Pacific. At present, there is nothing more transformative concerning the nature of jobs and the future of work than the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR)-a new era built on the use of more sophisticated robots and computing power and the automation of tasks once thought to be uniquely human (ADB 2018). The types of jobs workers need to sustain their livelihoods, the industries that power economic growth, even the societal expectations of what a job represents are all subject to constant change. Today’s labor markets are far different from those of decades past.

Jobs are in a constant state of evolution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
